|
|
|
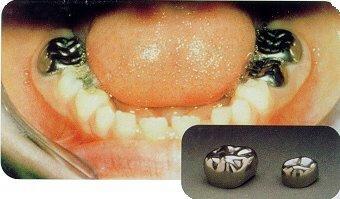
Stainless
steel crowns are most frequently used to restore
posterior teeth of children. They are bulky and generally do
not fit the tooth very well. They are pre fabricated and
need to be trimmed before being fixed. These prefabricated
crowns are relatively inexpensive and fairly quick to place,
and because of the nature of baby tooth enamel, are more
permanent than a regular filling would be. Large fillings in
baby teeth do not stand up very well to long term wear.
Stainless steel crowns are frequently placed on teeth that
have had pulpotomies as well, because by the time a baby
tooth needs a pulpotomy, the damage to the crown is so
severe that only a stainless steel crown is likely to remain
intact for the life of the tooth.
Fillings are adequate for back baby teeth if the decay is
not too extensive or too close to the nerve. They are not
adequate for teeth which have large or multiple fillings,
have decay so close to the nerve that removal of all the
decay would expose the nerve, or for any baby tooth in which
the nerve has been removed
Stainless steel crowns can be used on virtually any baby
tooth, but are best reserved for situations in which the
finished filling will take up more than half of the baby
tooth, the decay is very close to the nerve, and or if the
nerve has been removed. It is possible to place a stainless
steel crown over a baby tooth leaving a small amount of
decay in place to avoid killing the nerve. The decay
generally stops once the crown is placed. Large fillings on
baby teeth do not work well because of the nature of the
anatomy of the teeth and also because children tend to grind
their teeth naturally, and large fillings may not be
adequately retained under this type of stress. It is always
best to place a stainless steel crown on all baby teeth
which have had pulpotomies because these teeth tend to be
brittle and are likely to break, especially in children's'
mouths since they tend to grind their teeth mercilessly
 |
|